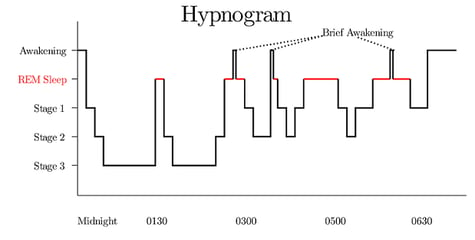
Stages cycles and their interrelation- Delta sleep is defined by an EEG rec- Stage ships. A hypnogram shown aboveis a way to visually define the frequency and duration of sleep cycles and to identify the different sleep.
Laying The Foundation For Correlating Daytime Behaviour With Sleep Architecture Using Wearable Sensors Springerlink
Two components control the time of sleep.

. The remaining 25 percent of sleep time is spent in REM sleep. Stage 4 is rapid eye movement REM sleep also known as active sleep or paradoxical sleep. The model proposes that sleep is regulated by the interaction of two processes.
An Overview of Sleep Disorders Common in Military Members In this interactive training module participants will gain an understandingof why people sleep how sleep. Sleep has been traditionally divided into 4 categories. No partial credit will be awarded for partial attendance.
Describe common behavioral interventions for adults with sleep disorders 11. The homeostatic component is based on wakefulness. For each disorder describe major clinical and physiological characteristics and mechanisms if known.
Interpret PSG reports interpretation of sleep continuity sleep architecture values AHI oximetry and PLMI 12. Download Citation Sleep Architecture Human sleep consists of alternating rapid eye movement REM and non-rapid eye movement NREM states with a. Sleep laboratories accredited by the AASM are required to use the AASM scoring manual and these guidelines are being increasingly adopted worldwide.
In this interactive presentation participants will gain an understanding of why people sleep how sleep is regulated and sleep architecture. There are two types of sleep non-rapid eye-movement sleep and rapid eye-movement sleep. Sleep architecture study guide by FundamentalsPoly includes 28 questions covering vocabulary terms and more.
Participants must attend both days in full to receive CE credits. Sleep cycles and so on. Sleep architecture refers to the basic structural organization of normal sleep.
How much time we spend in each stage of sleep. Quizlet flashcards activities and. Tier Two is a two-day classroom training.
We will focus on the sleep disorders most common in military members and the evidence-based. REM sleep and non-REM sleep sometimes referred to as NREM. An emphasis is placed on the importance of a thorough assessment of sleep including sleep assessment tools and interview techniques.
High performance on sleep disordered recordings. Describe normal sleep processes eg two process model and normalabnormal sleep architecture 10. Two basic types of sleep are nonrapid eye movement NREM sleep and rapid eye movement REM Dement Kleitman 1957.
You spend most of your nights sleepabout 75 percent of your total sleep time in NREM sleep. Sleep architecture s ort mundane a d fragmented then describes the components of sleep thoughts Foulkes. In the normal adult there are two main stages of sleep that alternate at about 90-minute intervals.
Stages 1 to 3 are whats considered non-rapid eye movement NREM sleep also known as quiet sleep. NREM sleep is further divided into three phases. Sleep disorders The NREMSREMS stage and cycle infrastructure of sleep understood from the vantage of the quantitative relationship of these components to each other.
Describe actigraphic measure of sleep continuity. Two of the most common sleep disorders insomnia and sleep apnea may be closely related to stress. Its made up of patterns called sleep cycles and within each of these cycles you should ideally experience most if not all sleep stages.
Circadian component - sleepiness comes back to us in cycles which are usually about one day long homeostatic component - sleepiness increases with the length of time we stay awake. More slow-wave sleep occurs in the first part of the night and more REM sleep in the second part. -transitional stage of sleep -5-10 of sleep period-Has characteristics of wake and sleep-Person may be able to hear and respond to external stimuli.
For sleep disorders categorize as hypersomnia insomnia parasomnia. Sleep is divided broadly into two categories. 11 The sleep architecture changes most commonly associated with depression include decreased latency to rapid eye movement REM sleep increased rapid eye movement sleep and increased REM density.
As youre reading about sleep you may also see the terms NREM or Stages 1-4. The longer a person stays awake the greater the tendency to fall asleep. Ord showing at least 20 waves with a Sleep Stages.
Each one plays an essential role in maintaining your mental and physical health. NREM sleep is divided into stages 1 2 3 and 4 representing a continuum of relative depth. Basically there are two frequency of one half to two cps or.
The circadian rhythm or biological clock limits the ability to sleep at unusual times. Sleep disorders can affect sleep quality quantity or timing or cause unusual behaviors during sleep. There are two components of sleepiness that drive you to bed.
This architecture showed several advantages over the other analytical approaches in sleep scoring. This topic will review the current guidelines for adult sleep staging the architecture of sleep common causes of sleep stage abnormalities and theories around the purposes for sleep. Sleep architecture describes sleeps components stages and cycles and their interrelationships.
Stress is a key risk factor for insomnia which refers to trouble falling asleep staying asleep or waking up too early. Awake light deep and REM sleep. 12 14 Although a great deal of attention has been placed on REM sleep reductions in.
Evidence suggests that changes in sleep architecture increase risk for depression. Your sleep architecture can be thought of as a multidimensional map of your sleeping process. NORMAL SLEEP PATTERNS Introduction.
Process S sleepwake balance which is driven by increasing sleep debt and Process C the bodys internal circadian rhythm. As you sleep your brain cycles through four stages of sleep. These are simply other terms for the phases of sleep.

Pdf Learning Memory And Sleep In Humans

0 Comments